Space-Age Medicine: NASA and SpaceX Partner to Investigate Heart Health in Zero Gravity
NASA and SpaceX Dragon to carry 3D heart cells and tissue to the space station for heart studies.
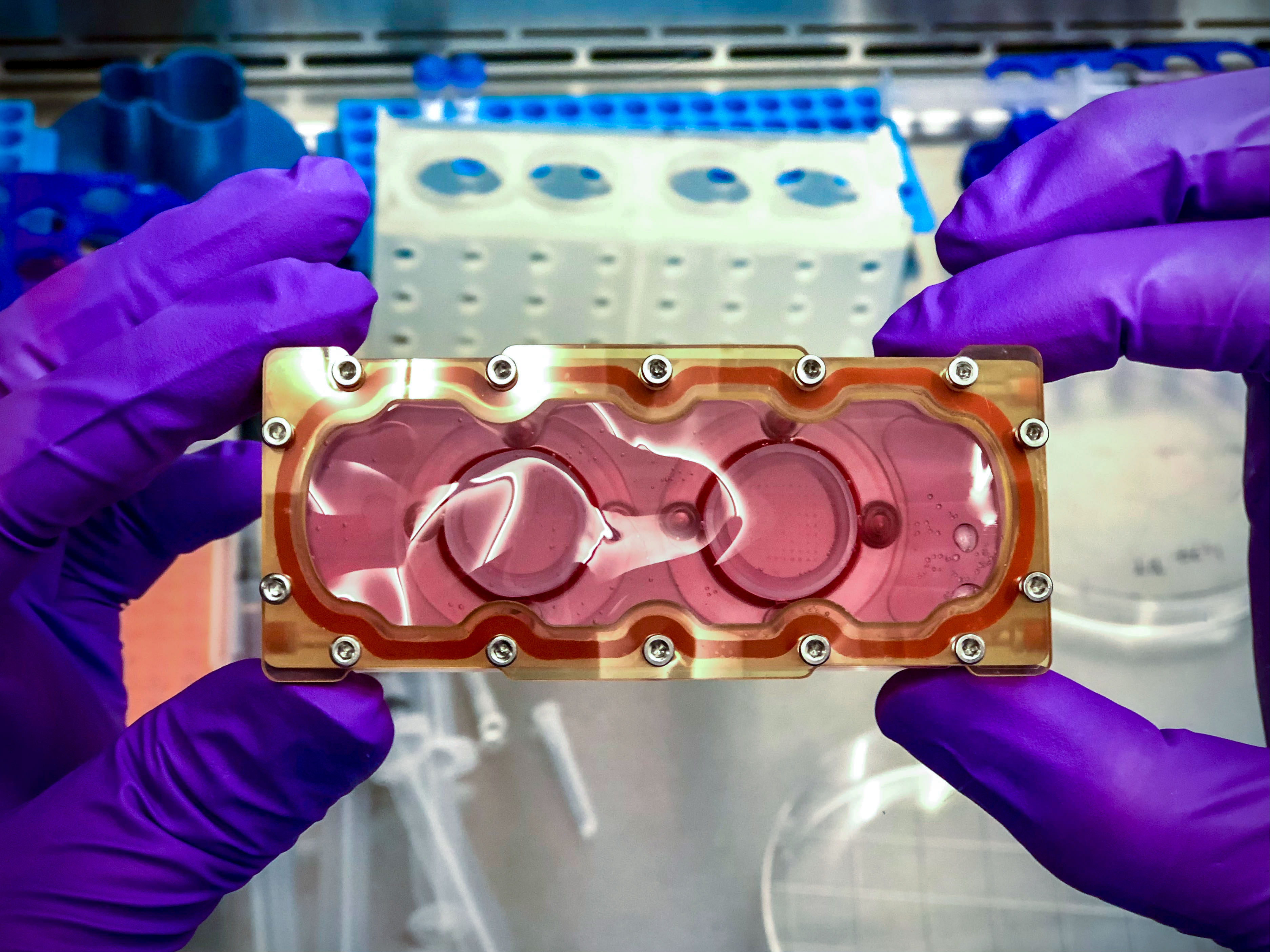
In a recent space mission, NASA and SpaceX collaborated to launch the Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station (ISS). The Dragon spacecraft was carrying 3D heart cells and tissue samples, which are expected to be used to develop treatments for heart issues. The heart cells and tissue were among the many experiments studying carbon dioxide and life in space that were aboard the spacecraft.
This space mission is not the first time that NASA and SpaceX have collaborated to transport biological samples to the space station. In previous missions, they have carried samples of tissue, cancer cells, and other biological materials to conduct experiments in space. The results from these experiments have been promising, leading to advancements in medical research and treatment.
One of the reasons for conducting experiments with heart cells and tissue in space is the unique environment in space. The lack of gravity in space creates conditions that cannot be replicated on Earth, making space an ideal environment for certain types of research. For example, the lack of gravity allows cells and tissues to grow and form into three-dimensional structures without the constraints of gravity. This ability to grow three-dimensional structures is essential for the development of heart tissue.
The 3D heart cells and tissue samples that were transported to the space station are expected to be used to develop treatments for heart issues. One of the areas of focus is regenerative medicine, which involves using the body's natural ability to regenerate tissue to treat heart conditions. Regenerative medicine has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of heart disease, which is one of the leading causes of death worldwide.
The experiments with the heart cells and tissue samples will also help researchers better understand the effects of space on the human body. Space travel is known to have many physiological effects on the human body, including changes to the cardiovascular system. By studying the effects of space on heart cells and tissue, researchers can develop strategies to minimize these effects and improve the health and safety of astronauts during space travel.
In addition to the experiments with heart cells and tissue, the Dragon spacecraft also carried out other experiments studying carbon dioxide and life in space. One of the experiments involved growing plants in space. The lack of gravity in space presents unique challenges to growing plants, but the results from this experiment could have significant implications for future space missions. The ability to grow plants in space could provide a sustainable source of food and oxygen for astronauts during long-duration missions.
The collaboration between NASA and SpaceX on this mission highlights the importance of public-private partnerships in advancing scientific research and technological innovation. NASA has a long history of conducting groundbreaking research and exploration, but partnerships with private companies like SpaceX have allowed them to push the boundaries even further.
In conclusion, the recent space mission by NASA and SpaceX to transport 3D heart cells and tissue to the space station is a significant milestone in the development of treatments for heart issues. The unique environment of space provides researchers with an ideal platform to conduct experiments that would not be possible on Earth. The results from these experiments could lead to advancements in regenerative medicine and improve the health and safety of astronauts during space travel. This mission is a testament to the power of public-private partnerships in advancing scientific research and technological innovation.
This space mission is not the first time that NASA and SpaceX have collaborated to transport biological samples to the space station. In previous missions, they have carried samples of tissue, cancer cells, and other biological materials to conduct experiments in space. The results from these experiments have been promising, leading to advancements in medical research and treatment.
One of the reasons for conducting experiments with heart cells and tissue in space is the unique environment in space. The lack of gravity in space creates conditions that cannot be replicated on Earth, making space an ideal environment for certain types of research. For example, the lack of gravity allows cells and tissues to grow and form into three-dimensional structures without the constraints of gravity. This ability to grow three-dimensional structures is essential for the development of heart tissue.
The 3D heart cells and tissue samples that were transported to the space station are expected to be used to develop treatments for heart issues. One of the areas of focus is regenerative medicine, which involves using the body's natural ability to regenerate tissue to treat heart conditions. Regenerative medicine has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of heart disease, which is one of the leading causes of death worldwide.
The experiments with the heart cells and tissue samples will also help researchers better understand the effects of space on the human body. Space travel is known to have many physiological effects on the human body, including changes to the cardiovascular system. By studying the effects of space on heart cells and tissue, researchers can develop strategies to minimize these effects and improve the health and safety of astronauts during space travel.
In addition to the experiments with heart cells and tissue, the Dragon spacecraft also carried out other experiments studying carbon dioxide and life in space. One of the experiments involved growing plants in space. The lack of gravity in space presents unique challenges to growing plants, but the results from this experiment could have significant implications for future space missions. The ability to grow plants in space could provide a sustainable source of food and oxygen for astronauts during long-duration missions.
The collaboration between NASA and SpaceX on this mission highlights the importance of public-private partnerships in advancing scientific research and technological innovation. NASA has a long history of conducting groundbreaking research and exploration, but partnerships with private companies like SpaceX have allowed them to push the boundaries even further.
In conclusion, the recent space mission by NASA and SpaceX to transport 3D heart cells and tissue to the space station is a significant milestone in the development of treatments for heart issues. The unique environment of space provides researchers with an ideal platform to conduct experiments that would not be possible on Earth. The results from these experiments could lead to advancements in regenerative medicine and improve the health and safety of astronauts during space travel. This mission is a testament to the power of public-private partnerships in advancing scientific research and technological innovation.